外观
一个reduce还能玩出这么多花样儿?中高级前端都知道的reduce函数高级用法
reduce 函数是 JavaScript 中的一个功能强大的高阶函数,它算是 JS 数组方法里面较为复杂的一个函数了。reduce 的灵活性在于它能够遍历数组的所有元素,根据提供的函数累积一个最终的返回值。reduce()方法可以应用的场景特别多,循环遍历能做的,reduce都可以做,比如数组求和、数组求积、统计数组中元素出现的次数、数组去重等等。
一、reduce的用法
reduce() 方法对数组中的每个元素按序执行一个由您提供的 reducer 函数,每一次运行 reducer 会将先前元素的计算结果作为参数传入,最后将其结果汇总为单个返回值。
第一次执行回调函数时,不存在“上一次的计算结果”。如果需要回调函数从数组索引为 0 的元素开始执行,则需要传递初始值。否则,数组索引为 0 的元素将被作为初始值 initialValue,迭代器将从第二个元素开始执行(索引为 1 而不是 0)。
注意: reduce() 对于空数组是不会执行回调函数的。
语法如下:
array.reduce(function(total, currentValue, currentIndex, arr), initialValue简洁语法:
reduce(callbackFn, initialValue)function(total,currentValue, index,arr):回调函数,必需。
total:上一次回调函数的返回值,第一次调用回调函数时,如果指定的初始值 initialValue,那么该参数值就是 initialValue,否则就是数组元素的第一个。
currentValue:数组中正在处理的元素。在第一次调用时,若指定了初始值 initialValue,那么当前处理的元素就是数组的第一个元素,否则的话就是第二个元素。
currentIndex:数组中正在处理的元素的索引。若指定了初始值 initialValue,则起始索引号为 0,否则从索引 1 起始。
array:用于遍历的数组。
initialValue:可选。传递给函数的初始值。也就是第一次调用回调函数时参数total,是否指定初始值将会影响其它几个参数的值。
reduce 方法的返回值就是遍历所有数组执行回调函数后的返回值。
二、reduce的使用场景
2.1 数组求和
日常开发基本使用中,最简单其实就是数组求和的场景了。代码如下:
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8];
const result = arr.reduce((total, currentValue) => {
return total + currentValue;
}, 0);
console.log(result); // 36按指定属性求和:
const arr = [
{ name: '张三', score: 98 },
{ name: '李四', score: 86 },
{ name: '王五', score: 90 },
];
const result = arr.reduce((total, currentValue) => {
return total + currentValue.score
}, 0);
console.log(result); // 274按照条件求和:
const arr = [
{ name: '张三', score: 93 },
{ name: '李四', score: 76 },
{ name: '王五', score: 80 },
{ name: '赵六', score: 65 },
];
const result = arr.reduce((total, currentValue) => {
return currentValue.score >= 80 ? total + currentValue.score : total;
}, 0);
console.log(result); // 1732.2 计算数组每个数据出现的次数
这种场景通常出现在算法题当中,借助 reduce 就可以简单实现它。其主要思路是通过键值对的形式巧妙的将出现的次数存储下来。
代码如下:
const arr = ['Allice', 'Bob', 'Tiff', 'Bruce', 'Bob', 'Jack', 'Allice', 'Bob'];
const result = arr.reduce((total, currentValue) => {
total[currentValue] = (total[currentValue] || 0) + 1;
return total;
}, {});
console.log(result);
// {Allice: 2, Bob: 3, Tiff: 1, Bruce: 1, Jack: 1}变形:
同样的道理,也可以统计字符串中每个字符的出现次数,只需把字符串使用split方法分割成数组即可。
const str = 'Hello World';
const result = str.split('').reduce((total, currentValue) => {
total[currentValue] = (total[currentValue] || 0) + 1;
return total;
}, {});
console.log(result);
// {H: 1, e: 1, l: 3, o: 2, " ": 1, d: 1, r: 1, W: 12.3 数组去重
想不到吧!reduce还能实现数组去重?是的!
过程如下:
- 初始化一个空数组;
- 将需要去重处理的数组中的第1项在初始化数组中查找,如果找不到(空数组中肯定找不到),就将该项添加到初始化数组中;
- 将需要去重处理的数组中的第2项在初始化数组中查找,如果找不到,就将该项继续添加到初始化数组中;
- ……;
- 将需要去重处理的数组中的第n项在初始化数组中查找,如果找不到,就将该项继续添加到初始化数组中;
- 将这个初始化数组返回。
代码如下:
const arr = [1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6];
const result = arr.reduce((total, currentValue) => {
if(!total.includes(currentValue)) {
total.push(currentValue)
}
return total;
}, []);
console.log(result);
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]2.4 数组扁平化
将初始值设置为了空数组,然后利用 concat 将数组中的每一项与初始值拼接,得到一个新的数组。
const arr = [['a', 'b'], ['c', 'd'], ['e', 'f']];
const result = arr.reduce((total, currentValue) => {
return total.concat(currentValue);
}, []);
console.log(result);
// ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']2.5 将二维数组转为对象
又没想到吧!将二维数组转化为对象,其过程为将初始值设置为了空对象,currentValue可以看做为[key, value],然后total[key] = value把键值放入total对象中。
const arr = [['name', '前端技术营'], ['age', '18'], ['sex', '男']];
const result = arr.reduce((total, [key, value]) => {
total[key] = value
return total;
}, {});
console.log(result);
// {name: '前端技术营', age: '18', sex: '男'}2.6 提取数组中的特定值生产新数组
const arr = [{id: 1, name: 'Tom'}, { id: 2, name: 'Jack' }, { id: 3, name: 'Anna' }]
const result = arr.reduce((total, currentValue) => {
return [...total, currentValue.name]
}, []);
console.log(result);
// ['Tom', 'Jack', 'Anna']2.7 合并数组对象
const arr = [{name: '前端技术营'}, { age: 18 }, { sex: '男' }];
const result = arr.reduce((total, currentValue) => {
return { ...total, ...currentValue }
}, {});
console.log(result);
// {name: '前端技术营', age: 18, sex: '男'}2.8 解析url参数
const url = 'https://www.test.com/index.html?name=Jack&id=123456&latitude=31.101109&longitude=121.51367';
const params = url.split('?')[1];
const result = params.split('&').reduce((total, currentValue) => {
const [key, value] = currentValue.split('=');
total[key] = value;
return total;
}, {});
console.log(result);
// {name: 'Jack', id: '123456', latitude: '31.101109', longitude: '121.51367'}2.9 反序列化参数
const stringifyData = (data = {}) => {
return Object.entries(data).reduce((total, currentValue) => {
return `${total}${currentValue[0]}=${encodeURIComponent(currentValue[1])}&`
}, Object.keys(data).length ? "?" : "")
.replace(/&$/, "");
};
const params = stringifyData({
name: "Jack",
id: '123456',
age: 18
});
const url = `https://www.test.com/index.html${params}`;
console.log(url);
// https://www.test.com/index.html?name=Jack&id=123456&age=182.10 求最大值、最小值
计算数组中的最大值或最小值,可以使用原生api Math.max()和Math.min(),当然我们也可以使用reduce来实现。
const array = [1, 10, 6, 8, 3, 9];
const max = array.reduce((max, num) => (max > num ? max : num));
console.log(max); // 10
const min = array.reduce((min, num) => (min < num ? min : num));
console.log(min); // 12.11 根据指定项分组
const arr = [
{ name: '小明', score: 96 },
{ name: '小华', score: 88 },
{ name: '小红', score: 92 },
{ name: '小刚', score: 100 },
{ name: '小李', score: 96 },
{ name: '小美', score: 90 },
{ name: '小芳', score: 100 },
]
const result = arr.reduce((total, currentValue) => {
const { score } = currentValue;
if(!total[score]) total[score] = [];
total[score].push(currentValue)
return total;
}, {})
console.log(result)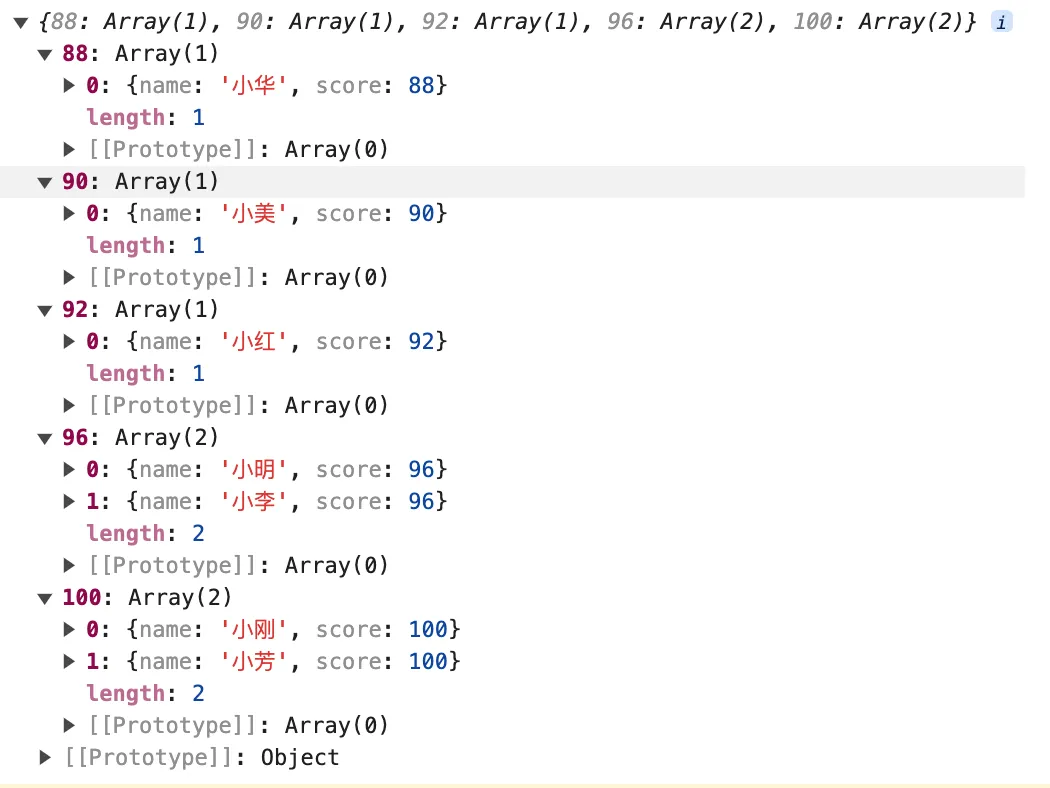
更复杂场景,多条件数据分类。
假设有一个包含人员信息的数组,每个人员对象有 age 和 gender 属性。现在我们想要根据人员的年龄和性别进行多条件分类。
const arr = [
{ name: 'Alice', age: 25, gender: 'female' },
{ name: 'Bob', age: 30, gender: 'male' },
{ name: 'Charlie', age: 25, gender: 'male' },
{ name: 'Dave', age: 35, gender: 'male' },
{ name: 'Eve', age: 25, gender: 'female' },
];
const result = arr.reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => {
const { age, gender } = person;
if (!accumulator[age]) {
accumulator[age] = {};
}
if (!accumulator[age][gender]) {
accumulator[age][gender] = [];
}
accumulator[age][gender].push(person);
return accumulator;
}, {});
console.log(result);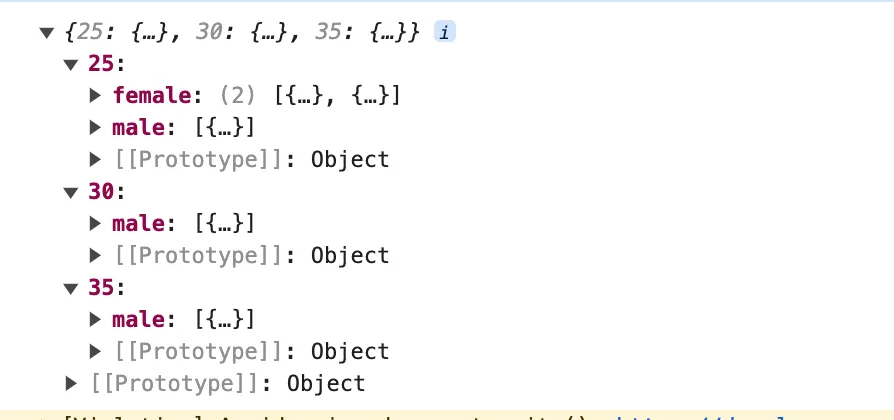
2.12 管道函数
当结合其他高阶用法时,reduce 可以应用于非常复杂的场景。其中一个非常复杂的场景是实现函数组合或管道。管道(Pipe)是指输入一个值,依次经过管道(有序的函数运算)后输出这个值,也是函数编程的核心思想。
函数组合是一种将多个函数合并成一个新函数的技术,其中每个函数的输出都是下一个函数的输入。我们可以使用 reduce 和函数组合技术来实现函数管道,将一系列函数应用于数据并依次传递结果。
function add10(num) {
return num + 10;
};
function multipl2(num) {
return num * 2;
};
function divide3(num) {
return num / 3;
};
const compose = (fns) => (initialValue) => fns.reduce((previous, current) => current(previous), initialValue);
const calculate1 = compose([add10, divide3]);
const calculate2 = compose([divide3, add10, multipl2]);
// 先加10,在除以3
console.log(calculate1(20)); //10
// 先加10,在除以3,最后乘以2
console.log(calculate2(9)); //26三、总结
reduce 是数组的归并方法,与forEach、map、filter等迭代方法一样都会对数组每一项进行遍历,但是reduce可同时将前面数组项遍历产生的结果与当前遍历项进行运算,这一点是其它迭代方法无法企及的。
reduce除了以上介绍的使用场景外,还有很多其它使用场景,有兴趣的朋友可以研究一下。
